Rollax thermal paper consists of base paper and some special coatings. A pre-coating layer and a thermal layer are applied to the surface side. A cover layer can be applied to the thermal layer in order to impart high durability to the thermal printed image. The backsheet can also be coated to improve printability and backside protection from adhesives.
Thermal Printing
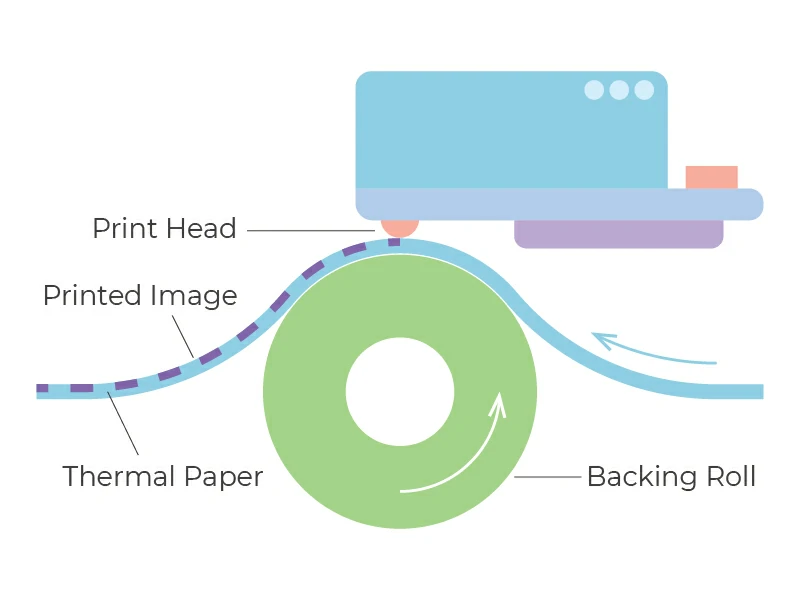
Thermal paper is a recording medium that is printed by the heat from a thermal printer. The image is produced without ink by heat as the selected area of thermal paper passes through the thermal printhead.
Images are created by transferring heat (heat energy) directly to thermal paper. Thermal paper has a coating that turns black when exposed to heat. No ribbon, toner, or ink cartridges are required to record information on thermal paper. Thermal printing is done using a small, compact thermal printer that does not require much maintenance. Due to its reliability and convenience, thermal paper is used in many applications such as labels, tickets, POS receipts, and medical records.
Thermal Paper Structure
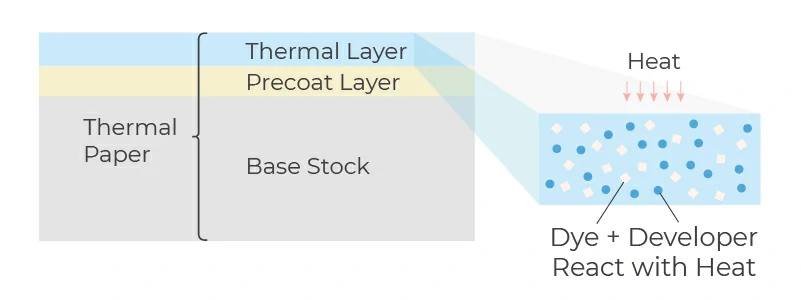
The thermal paper consists of base paper and a few special coating layers. On the surface side (the recording side), the precoat layer and the thermal layer are coated.
Base Paper - The first layer of thermal paper is a base paper specially developed for thermal paper technology. The base paper is coated with a thermal layer.
Precoat layer - Precoat layer improves insulation, smoothness, uniformity, and thermospheric fixation.
Thermal layer - The purpose of this layer is to create a thermal responsive image. In reality, this layer of chemicals such as dyes, developers and sensitizers causes the paper to blacken in the heated areas.
Topcoated Thermal Paper Structure
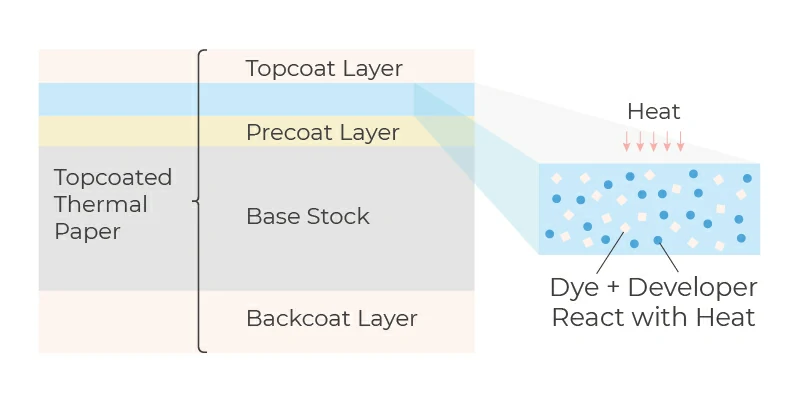
If high durability of the heat-printed image is required, a topcoat is applied to the thermal layer. In addition, the backside can be coated to improve both printability and backside protection from adhesives.
Topcoat layer - The topcoat layer protects the thermal layer from water, oil, solvent, humidity, scratches, etc..
Backcoat layer - The backcoat layer is applied for de-curling, antistatic electricity treatment, and back-barrier against adhesive.
Thermal paper features
The main function of thermal paper is “thermal printing”. Therefore, in addition to normal paper characteristics such as basis weight, thickness, and strength, the quality of thermal printing and image stability are also important.
In addition, thermal paper also requires pre-printability using traditional printing methods such as flexography and offset.
